Direct Speech and Reported(Indirect) Speech
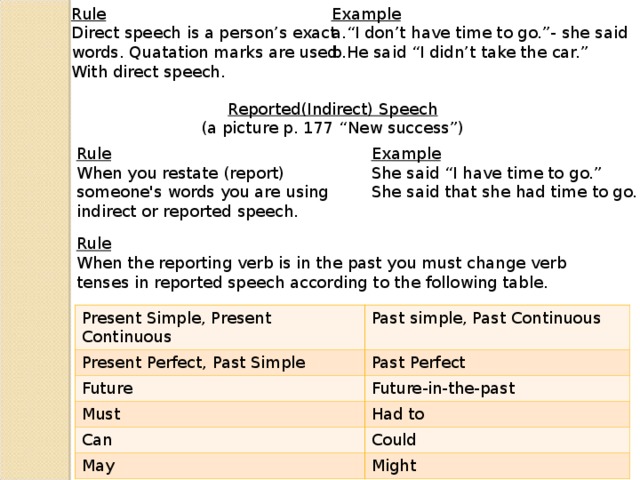
Rule
Direct speech is a person’s exact
words. Quatation marks are used
With direct speech.
Example
“ I don’t have time to go.”- she said He said “I didn’t take the car.” Reported(Indirect) Speech
(a picture p. 177 “New success”)
Rule
When you restate (report)
someone's words you are using
indirect or reported speech.
Example
She said “I have time to go.”
She said that she had time to go.
Rule
When the reporting verb is in the past you must change verb tenses in reported speech according to the following table.
Present Simple, Present Continuous
Present Perfect, Past Simple
Past simple, Past Continuous
Future
Past Perfect
Future-in-the-past
Must
Can
Had to
May
Could
Might
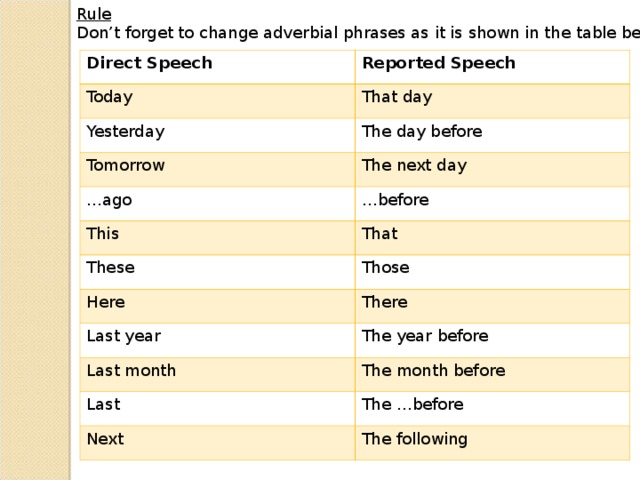
Rule
Don’t forget to change adverbial phrases as it is shown in the table below
Direct Speech
Reported Speech
Today
That day
Yesterday
The day before
Tomorrow
The next day
… ago
… before
This
That
These
Those
Here
There
Last year
The year before
Last month
The month before
Last
The …before
Next
The following
Reported Statements
Verb (that)
(Say, claim, admit, explain, agree, complain, reply, deny etc.)
Practice 1
“ John is sick,” she said She said that John was sick.
2. “I have already read this book”, Nick said
3. “I always have lunch at the same place”, her sister said.
4. “I will pick you up in front of the school”, she said to her son.
5. “You have to do it”, he said to his daughter.
6. “They got up early”, Chris said.
7. “We saw them in the theatre”, he said.
8. “I can get there around noon”, Steve said.
9. “He must pay the gas bill”, she said.
10. “It may rain soon”, the granny said.
Practice 2
“ I can do my homework myself.” (The pupil said…) “ I have no time for lunch today.” (The boy said to his mother…) “ It’s cold.” (She said…) “ I haven’t been to the cinema for ages.” (He said…) “ My son watches TV very often.” (Mrs. Smith said…) “ It takes about three ours to drive to Cambridge.” (He explained…) ‘ I’ll leave work early.” (Angela said…) “ Maria doesn’t understand English.” (I said…) “ I wanted to watch this film.” (She said…) There is too much advertising on TV.” (He said…) Practice 3
“ I’ll see you tomorrow.” She said… “ I’ll phone you this evening.” He said… “ My uncle died last week.” He told me… “ This meat tastes funny.” She said… “ I’m leaving now.” He told us… “ I overslept this morning.” She told him… “ The train leaves at 11.00 tonight.” I was told… “ Pete phoned me yesterday.” He said Pete… “ My brother’s arriving here today.” She said… ‘ You ought to see the doctor.” He advised me…
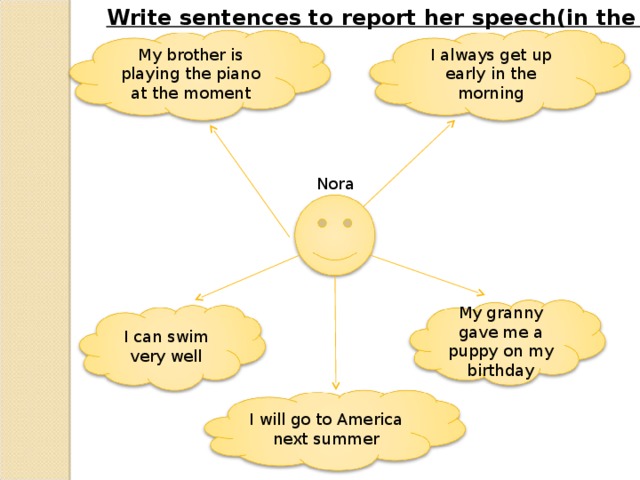
Write sentences to report her speech(in the past)
I always get up early in the morning
My brother is playing the piano at the moment
Nora
My granny gave me a puppy on my birthday
I can swim very well
I will go to America next summer
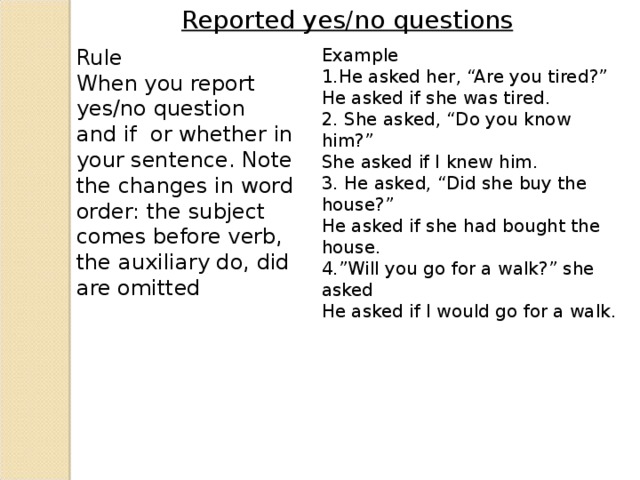
Reported yes/no questions
Rule
When you report yes/no question
and if or whether in your sentence. Note the changes in word order: the subject comes before verb, the auxiliary do, did are omitted
Example
He asked her, “Are you tired?” He asked if she was tired.
2. She asked, “Do you know him?”
She asked if I knew him.
3. He asked, “Did she buy the house?”
He asked if she had bought the house.
4.”Will you go for a walk?” she asked
He asked if I would go for a walk.
Practice 1
Relate this yes/no questions using reported speech.
1. “Is he sick?” she asked.
She asked if he was sick.
2. “Were they late?” the teacher asked.
3. “Can you go with her?” Carrie asked.
4. She asked me, “Do you want to leave?”
5. He asked, “Did you really do that?”
6. “Will it take long to get to London?” Sandy asked.
7. “Have you had dinner yet?” she asked her son.
8. “Is it raining?” he asked.
9. Everyone in the class asked, “Do we have to take the test?”
10. “Is he staying at a hotel?” she asked.
Practice 2
“ Are you a doctor?” (He asked her…) “ Does she know what’s she doing?” (I wondered…) “ Can you swim?” (He asked me…) “ Is John studying for examination now?” (I asked…) “ Will you be able to finish by tomorrow?” (She asked…) “ Are you interested in foreign news?” (I asked him…) “ Did you have holidays last year?” (She asked him…) “ Are there many books in the box?” (The teacher asked…) “ Have you been to Britain?” (He asked his friend…) “ Do you go to bed at a fixed time?” (John asked her… Practice 3
Turn the sentences into indirect questions, beginning I wondered.
Do you like me? Will I be ready in time? Is there any food in the house? Is service included or not? Can I pay by cheque? Does my hair look funny? Has the postman been? Do they speak English? Am I doing the right thing? Is the meeting on Tuesday or Wednesday?
Reported wh- questions
Rule
Wh- questions are questions that start with one of the wh- words: when, why, where, who, whose.
In the reported wh- questions the subject goes before the verb the auxiliary do and did are omitted unless it forms the negative clause.
Follow the rule of sequence of tenses, if the main verb is in the past tense!
Example
1. “Why did he leave?” he asked.
He asked why he had left.
2. “What are you doing?” I asked him.
I asked him what was he doing.
3. “Where do you live?” he asked me.
He asked me where I lived.
4. “Who is she?” I wondered.
I wondered who she was.
Practice 1
1. “Why do you go there?” she asked her friend.
She asked her friend why she went there.
2. “Who invented the necktie?” my friend asked.
3. “Where did they leave the car?” they asked.
4. “What did he put in the coffee?” his mother asked.
5. “Whose car are you driving?” she asked me.
6. “When do you have to go?” John asked his friend.
7. “What kind of test will it be?” she asked.
8. “How long is it going to rain?” he asked.
9. “Where can I park my car?” a stranger asked.
Practice 2
“ Why hasn’t he locked the front door?” (The policeman asked…) “ Where are you going to spend your holidays?” (Mike asked…) “ Why didn’t Isabel phoned me?” (Her brother asked…) “ What will you do when you finish school?” (Jenifer asked…) “ Where is the nearest shop?” (The old man asked the policeman…) “ Why do your parents live in Greece?” (She asked me…) “ How many people know about plan?” (He asked…) “ What time does the next bus leave?” (He asked…) “ How long have you known this woman?” (I asked her…) “ What were your favorite subjects at school?” (My uncle asked me…)
Practice 3
Turn these sentences into reported questions beginning I wondered
How often does Ann go shopping? What time is the meeting? When does the last train leave? Where do they keep the money? Why are all windows open? How does she know my name? What’s Peter’s address?
Reported speech: Imperative Sentences (Reported orders and Requests)
Presentation
Rule
Imperative sentences in reported speech are changed to infinitive phrases. Use tell (ask) + an indirect object + an infinitive
or
Tell (ask) + an indirect object + not + an infinitive
Example
“ Be careful,” he said to her
He told her to be careful.
“ Live for the day,” she told Rob
“ Open the door, please,” he asked her.
He asked her to open the door.
“ Don’t go there,” he said
He told her not to go there.
“ Don’t eat too many sweets, please,” she said to her son.
She asked her son not to eat too many sweets.
Practice
Change these imperative sentences in reported speech
1.”Drive carefully,” she said to him.
She told him to drive carefully.
2. “Be home at ten,” he said to his son.
3. He said many times to his daughter “Do your best”.
4. As I was leaving, he said, “Lock the door.”
5. “Don’t forget to take your raincoat,” he said to her daughter.
6. “Don’t be afraid,” she advised her brother.
7. “please don’t shout,” she asked them.
8. “Read the letter, please,” he said to his friend.
#1
Use the reported speech
Production
John said: “I’m sorry to disturb you, Eliza.” He said: “Where is Jill going?” Sally said: “I would like to buy it.” Robby asked: “Bobby, do you know “Old Barn”? It’s on the Shrewsbury Road”. The doctor asked: “How do you feel?” “ Will you be free tomorrow?” Colin asked Richard . Don’t open the door or answer the phone” said her parents. “ Why hasn’t he locked the front door?” the policeman asked. Tom said: “Jerry has been my best friend since our early childhood”. “ Where is the nearest bus stop?” The old man asked the policeman. The teacher said to us: “Be quiet, please.” “ Could you show me these jeans, please?” said the boy. “ Ann’s sister did nothing except complained” remarked Tom.
#2
What did they actually say. Write the sentences down in the direct speech.
Karen’s father made it clear that she should go to the station immediately. Paul asked Robert whether he had seen his glasses anywhere. Mrs. Turner said that she hadn’t seen Tom that day. Mr. Webster told his wife that she shouldn’t forget her handbag. The waiter said that there wouldn’t be enough chops for everybody. Paul said he was going to spend holiday in a Spain. Mother told me to take an umbrella because it was going to rain. He said I would not win the race if I did not train hard. The old man asked me to show him the way to the station. The boss asked when I had posted the letters.
#3
Write the sentences in the reported speech using the following verbs of reporting: say, tell, explain, advise, remind, order, ask, want, to know.
Anne: “I think science fiction stories are nonsense”. Alex to Norman: “I found a purse in the telephone box yesterday”. Mr. Smith to his wife: “It’s time to go home”. The Jonsons: “We had a marvelous holiday in Spain” Pauline: “I’m going to see my grandparents tomorrow”. Paul: “I was enjoying my visit to London very much”. Laurel and Kate: “We were here a year ago”. Mr. Nelson: “It’s rather cold today”. Marian to her mother: “I’m not going to help Tom this time. He can do it himself.” The driver to the policeman: “Can you tell me the way to the lake, please?” The teacher to Chris: “Why haven’t you done your homework, Chris?” The teacher to Mrs. Webb: “Don’t worry about your daughter, Mrs. Webb”. The friend: “Don’t forget your umbrella, Diana”. Susan to Bill: “Did you post the letter this morning?” The policeman to the driver: “Drive on the left-hand side, please.”
#4
1) Change into reported speech
Askar said: “We went to Bayterek last week”
Askar said that we went to Bayterek last week. Askar said that they had gone to Bayterek the previous week. Askar said that they had been to Bayterek last week. Askar said that we had been to Bayterek last week. Askar said that they went to Bayterek last week. 2) Choose the correct sentence
He said that he will return tomorrow. He said that he shall return tomorrow. He said that he should return tomorrow. He said that he would return the next day. He said that he return the next day. 3) Change into reported speech
“ Have you found the book?” she asked me.
She asked me if I have found the book. She asked me whether have I found the book. She asked me if I had found the book. She asked me whether I found the book. She asked me if I found the book.
4) Change into reported speech
“ Where did you find the pen?” Ben asked.
Ben asked where you had found the pen. Ben asked where I had found the pen. Ben asked where had I found the pen. Ben asked me where did I found the pen. Ben asked where I found the pen. 5) Change into reported speech
“ Where does Helen live?” Jane asked.
Jane asked where Helen lives. Jane asked where did Helen lives. Jane asked where Helen lived. Jane asked where does Helen live. Jane asked where Helen had lived.
6) Change into reported speech.
“ When were you born?” he asked me.
He asked me where I had been born. He asked me where was I born. He asked me where I was born. He asked me where did I born. He asked me where had I been born. 7) Choose the correct sentence
She told him don’t open the door. She told him not to open the door. She told him didn’t open the door. She told him not open the door. She told him not to open the door.