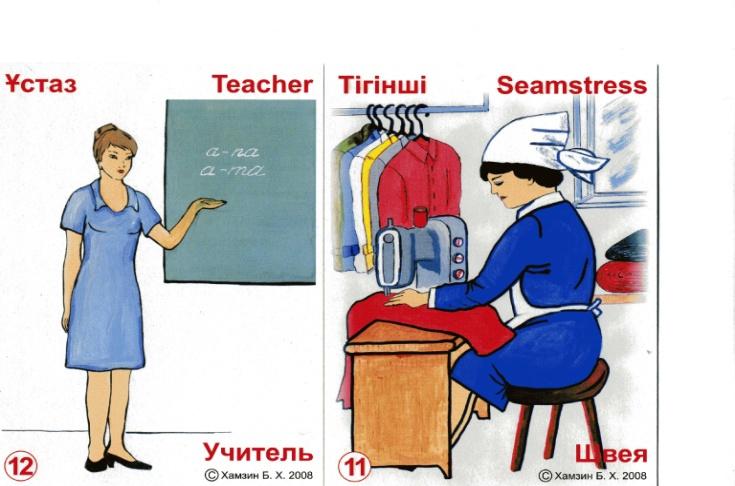
2-желтоқсанда 6 сыныпқа "Types os schools" атты тақырыпта ашық сабақ оздырылды. сабақта оқушылар лото таңдау арқылы екі топқа бөлініп, "Миға кері шабуыл" әдісі арқылы мектеп түрлері, сан есім түрлерін меңгерді.Сонымен қатар "Бинго", "крестиктер мен нөлдіктер" ойыны ойналды.
Создайте Ваш сайт учителя Видеоуроки Олимпиады Вебинары для учителей
"Types of schools"
Вы уже знаете о суперспособностях современного учителя?
Тратить минимум сил на подготовку и проведение уроков.
Быстро и объективно проверять знания учащихся.
Сделать изучение нового материала максимально понятным.
Избавить себя от подбора заданий и их проверки после уроков.
Наладить дисциплину на своих уроках.
Получить возможность работать творчески.
Просмотр содержимого документа
«6 кмж»
Просмотр содержимого документа
«ан»
Просмотр содержимого документа
«такырып»
Просмотр содержимого документа
«тапсырмалар»
Просмотр содержимого документа
«текст-2»
Просмотр содержимого документа
«текст»
Похожие файлы
Полезное для учителя
Распродажа видеоуроков!
1860 руб.
2660 руб.
1880 руб.
2690 руб.
1880 руб.
2690 руб.
1760 руб.
2510 руб.
ПОЛУЧИТЕ СВИДЕТЕЛЬСТВО МГНОВЕННО
* Свидетельство о публикации выдается БЕСПЛАТНО, СРАЗУ же после добавления Вами Вашей работы на сайт
Удобный поиск материалов для учителей
Проверка свидетельства
 in my
in my