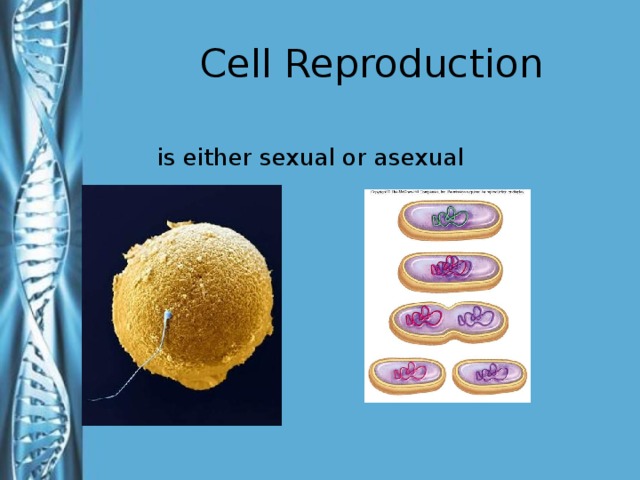
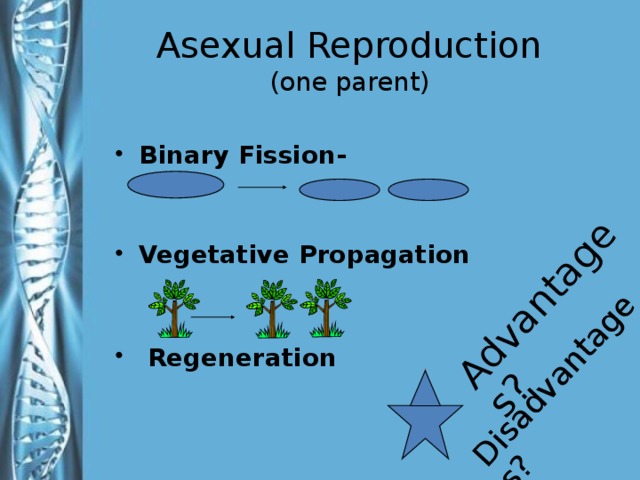
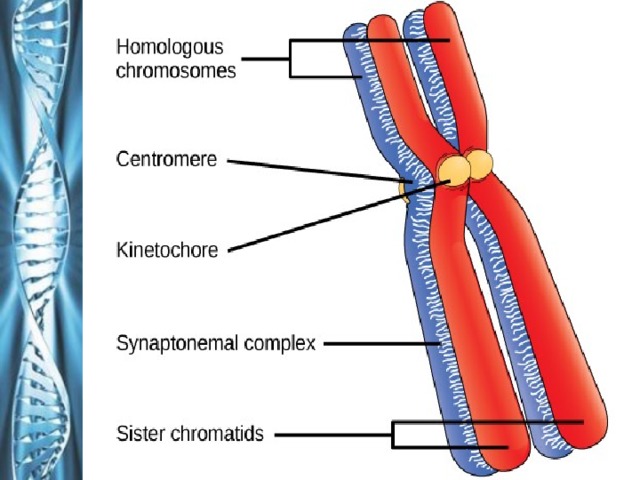
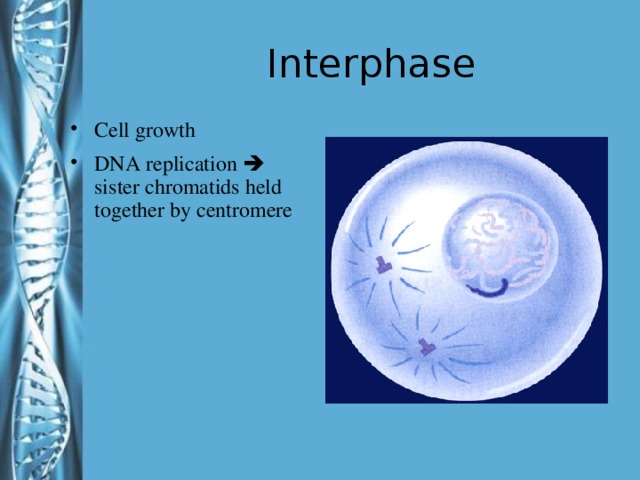
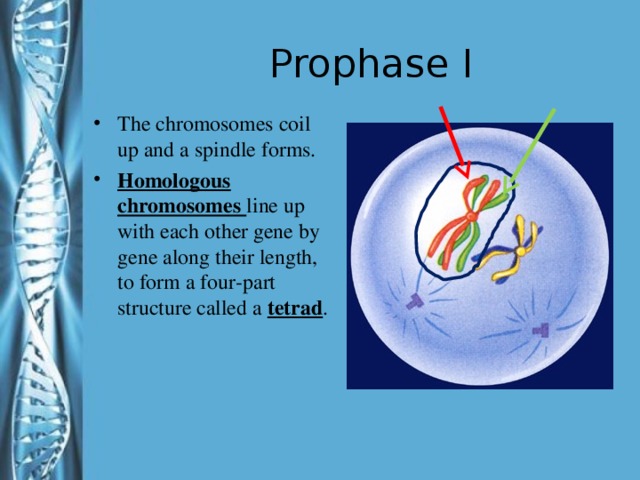
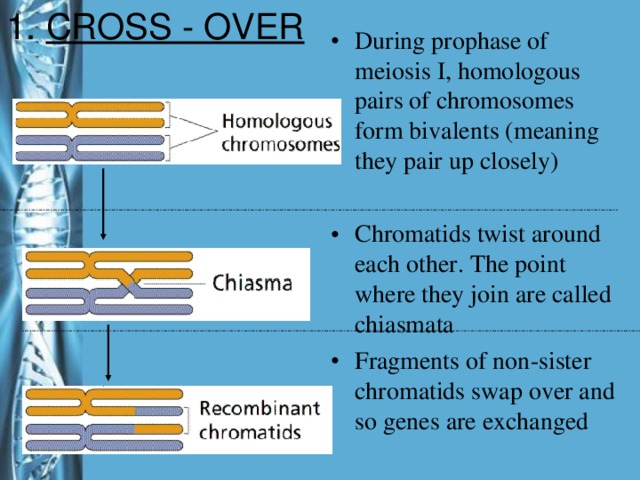
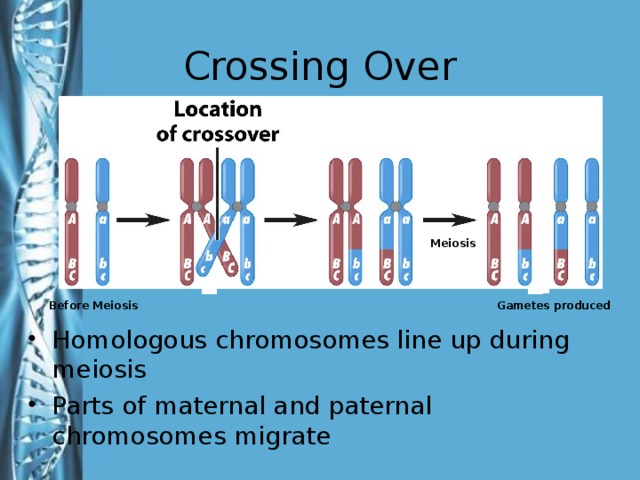
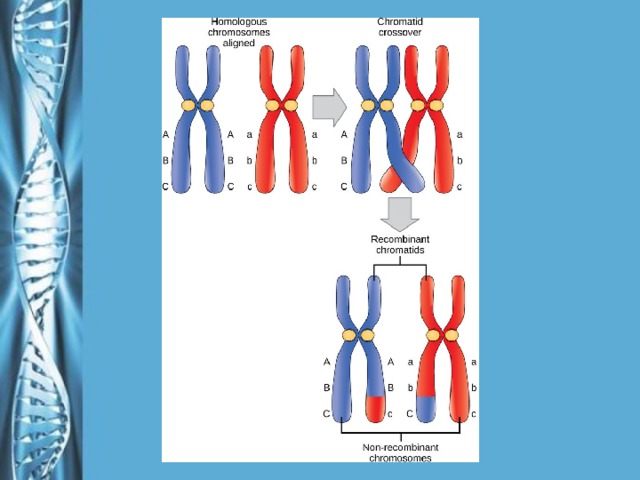
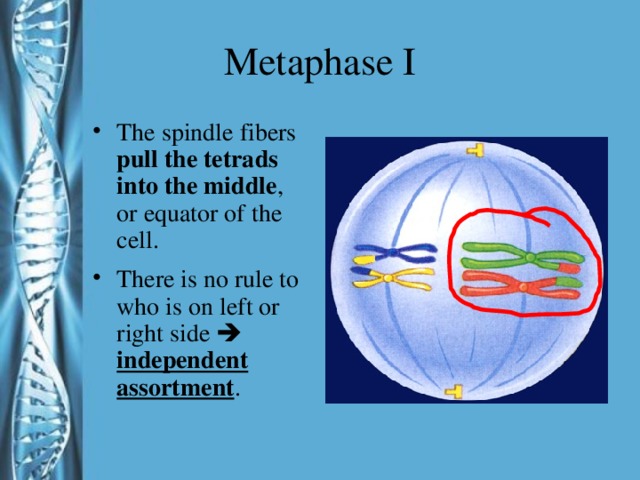
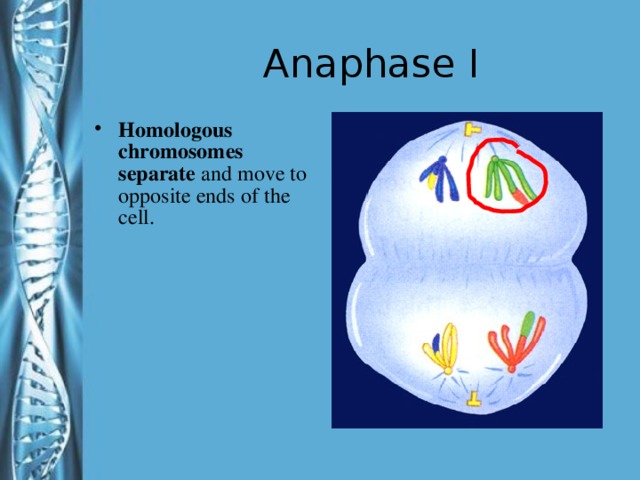
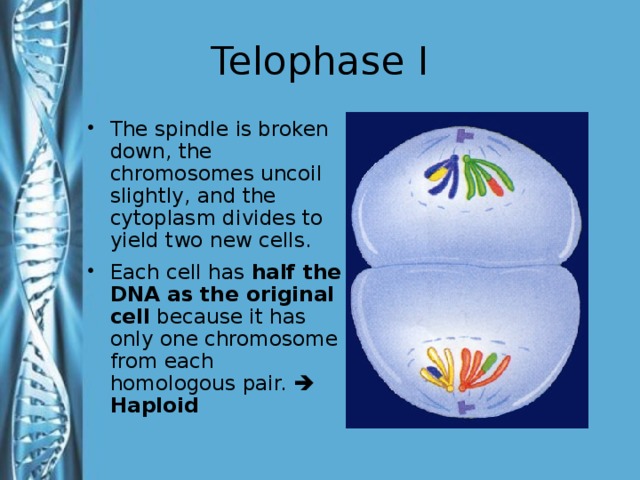
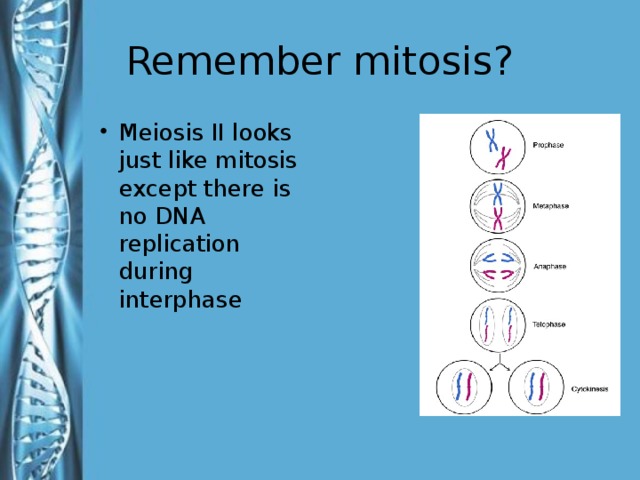
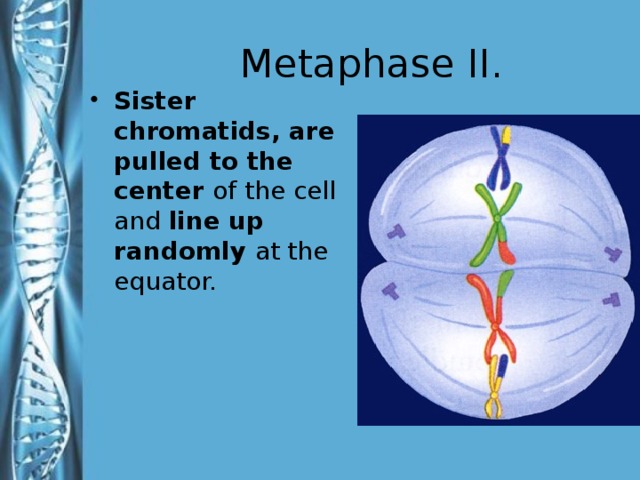
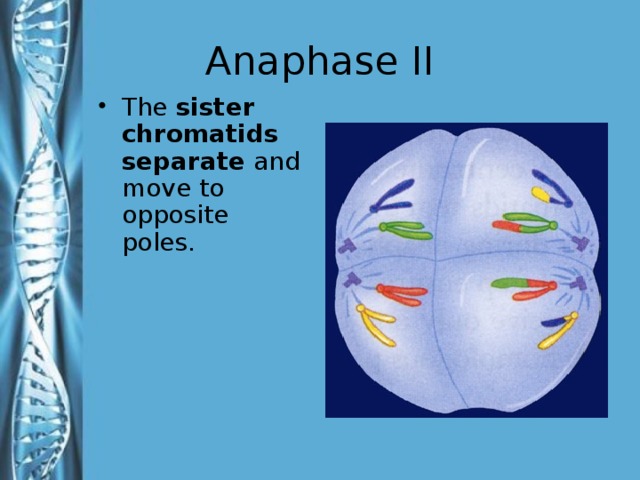
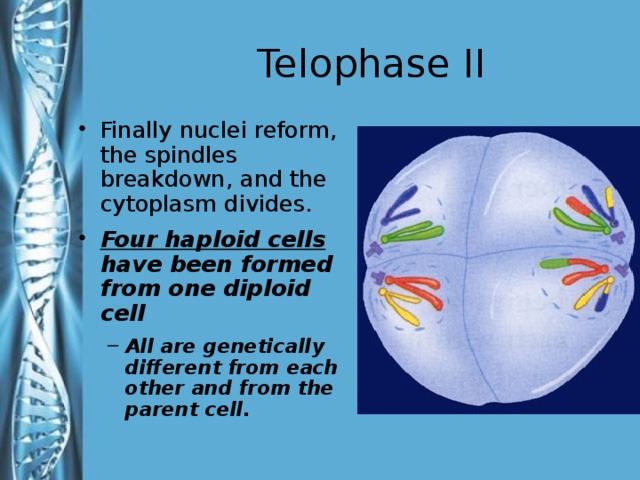
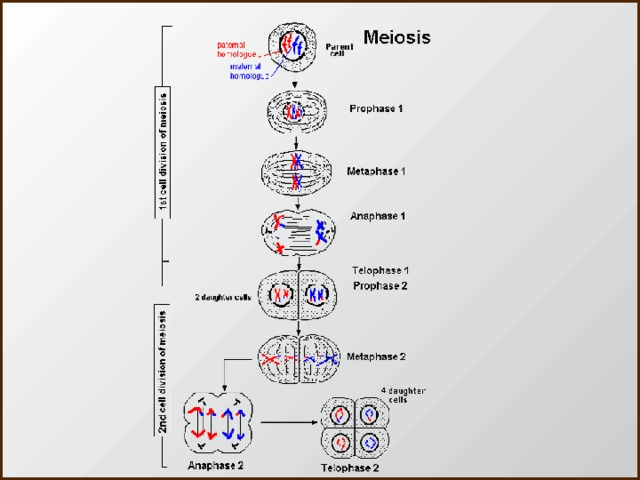
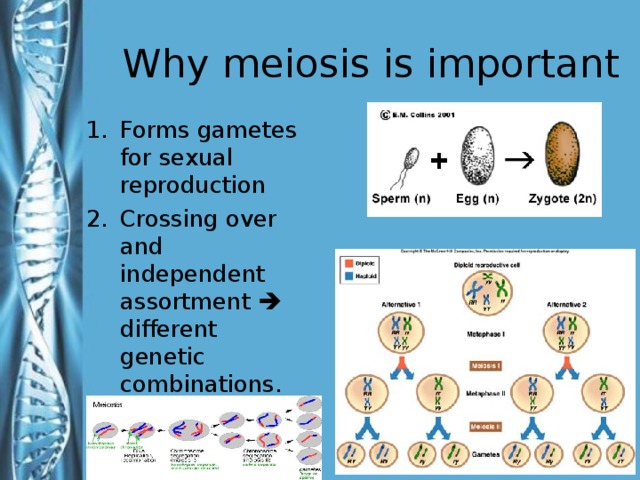
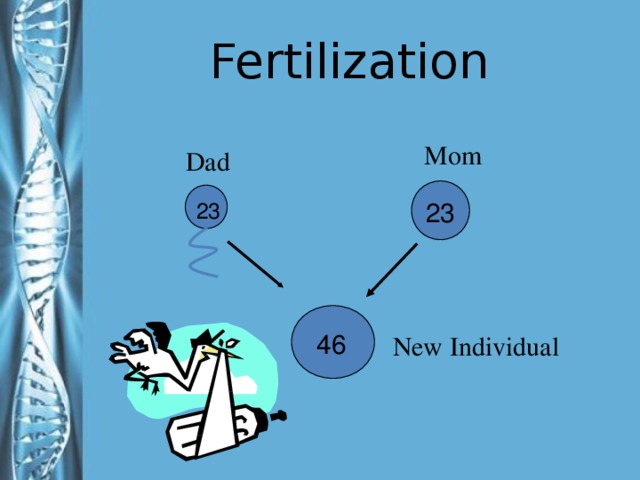
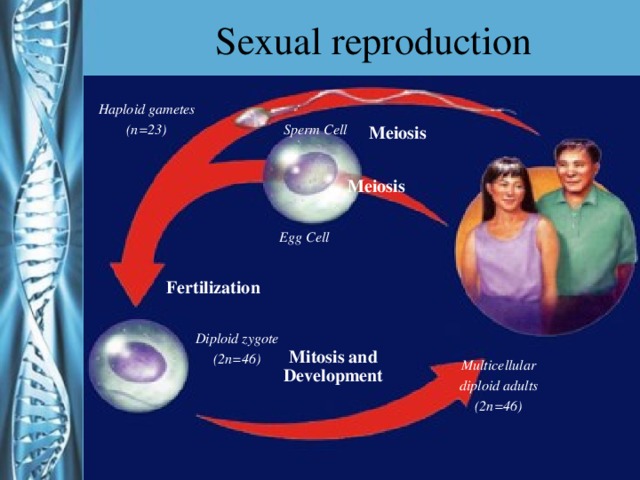
Describe the phases of meiosis and the mechanisms of recombination of genetic material during meiosis
Создайте Ваш сайт учителя Видеоуроки Олимпиады Вебинары для учителей
How it develops and progresses.
Вы уже знаете о суперспособностях современного учителя?
Тратить минимум сил на подготовку и проведение уроков.
Быстро и объективно проверять знания учащихся.
Сделать изучение нового материала максимально понятным.
Избавить себя от подбора заданий и их проверки после уроков.
Наладить дисциплину на своих уроках.
Получить возможность работать творчески.
Просмотр содержимого документа
«how it develops and progresses.»
Полезное для учителя
Распродажа видеоуроков!
2000 руб.
2860 руб.
1770 руб.
2530 руб.
1970 руб.
2820 руб.
2050 руб.
2930 руб.
ПОЛУЧИТЕ СВИДЕТЕЛЬСТВО МГНОВЕННО
* Свидетельство о публикации выдается БЕСПЛАТНО, СРАЗУ же после добавления Вами Вашей работы на сайт
Удобный поиск материалов для учителей
Проверка свидетельства