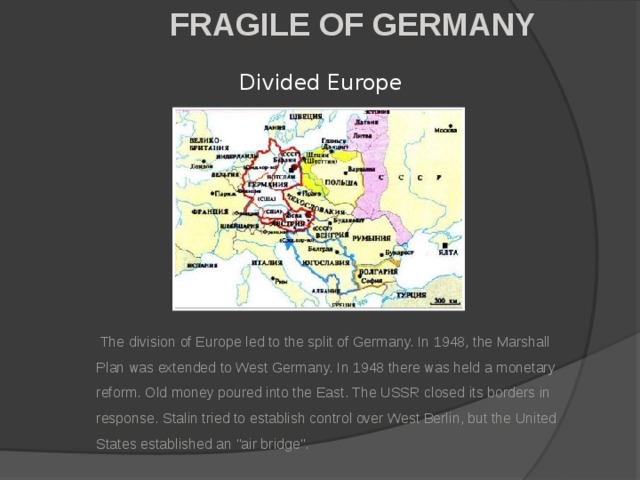
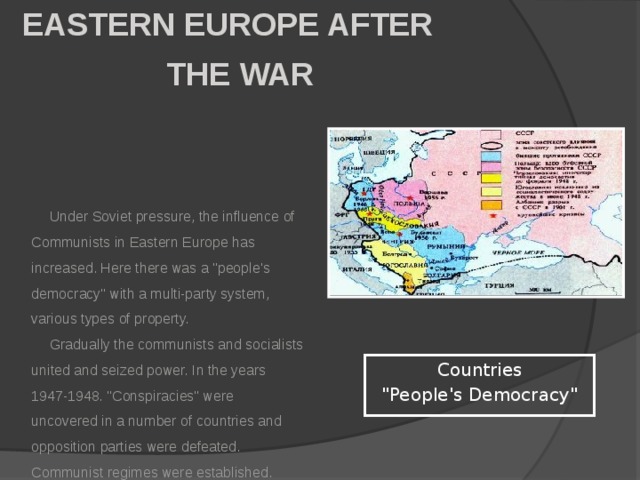
Данная презентация может быть использована как учителями, так и учениками в качестве иилюстративного материала для обычного урока или внеклассного мероприятия на тему "Войны 21-го века".
Создайте Ваш сайт учителя Видеоуроки Олимпиады Вебинары для учителей
Презентация по английскому языку на тему "Войны 21-го века" (9 класс)
Вы уже знаете о суперспособностях современного учителя?
Тратить минимум сил на подготовку и проведение уроков.
Быстро и объективно проверять знания учащихся.
Сделать изучение нового материала максимально понятным.
Избавить себя от подбора заданий и их проверки после уроков.
Наладить дисциплину на своих уроках.
Получить возможность работать творчески.
Просмотр содержимого документа
«Презентация по английскому языку на тему "Войны 21-го века" (9 класс)»
Полезное для учителя
Распродажа видеоуроков!
1880 руб.
2690 руб.
2160 руб.
3080 руб.
1970 руб.
2820 руб.
1880 руб.
2690 руб.
ПОЛУЧИТЕ СВИДЕТЕЛЬСТВО МГНОВЕННО
* Свидетельство о публикации выдается БЕСПЛАТНО, СРАЗУ же после добавления Вами Вашей работы на сайт
Удобный поиск материалов для учителей
Проверка свидетельства