| Course progress: TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS Chemical reactions are changes in which new substances are formed. During these changes, substances may break down into simpler substances or may exchange parts. Additionally, some substances may combine to yield a more complex substance. Chemical reactions can be classified as follows: combination, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, combustion, endothermic and exothermic reactions. COMBINATION REACTIONS
Reactions in which simpler substances combine to make a more complex one is called combination reaction. Combination reactions can be illustrated as: 
Example:
Other examples: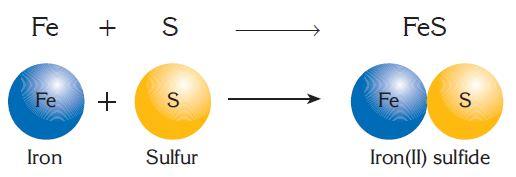 S + O2 → SO2 2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3 SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
Write and balance the equations for the reactions of lithium, aluminum and calcium with oxygen.
When these elements react with oxygen, oxides of the elements will be produced, Li2O, Al2O3 and CaO. Balanced equations for the formations of these compounds are:
4Li + O2 → 2Li2O 4Al + 3O2 → 2Al2O3 2Ca + O2 → 2CaO
DECOMPOSITION REACTIONS Reaction in which complex substance breaks down to simpler substance is called decomposition reaction. Decomposition reaction can be illustrated as: 
Example: 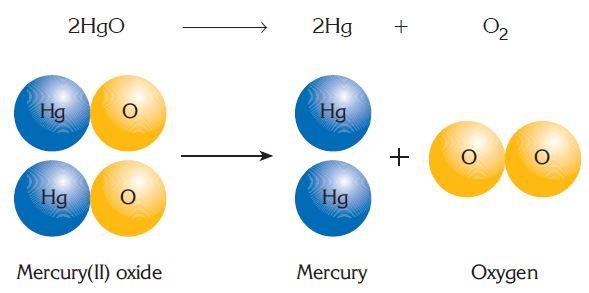 Other examples: 2H2O(l) → 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2KClO3→ 2KCl + 3O2 2NaCl(l) → 2Na(l) + Cl2(g) 2Ag2O → 4Ag + O2
SINGLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS Reactions in which one element displaces another one are called single displacement reactions. Single displacement reactions can be illustrated as:  Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → Cu(s) + ZnSO4(aq)
Zinc + Copper (II) sulfate → Copper + Zinc sulfate
NiO(s) + C(s) → Ni(s) + CO(g) Cu2O(s) + CO(g) → 2Cu(s) + CO2(g) However, if you immerse another piece of zinc into sodium chloride solution, no reaction will take place, because zinc is less active than sodium:
Zn(s) + NaCl(aq) ⎯⎯→ no reaction  Such single displacement reactions may also take place between nonmetals. For example, chlorine is more active than bromine, so chlorine may react with sodium bromide:
2NaBr(aq) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(aq) + Br2(l)
Complete and balance the following equations:
a. MgO + C → b. Al2O3 + H2 → c. PbO + CO → d. Ba + H2O →
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTION In a double displacement reaction, two parts in different compounds displace to form two new compounds. In such reactions, two reactants yield two products. Double displacement reaction can be illustrated as:  KCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) → KNO3(aq) + AgCl(s) Potassium chloride + Silver nitrate → Potassium nitrate + Silver chloride
COMBUSTION REACTIONS Combustion reaction is a chemical reaction between substances, usually including oxygen and usually accompanied by the generation of heat and light in the form of flame. Example: CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS In this type of chemical reaction, energy is produced as heat, and is noted on the products’ side (right). For instance, the burning of coal produces a quantity of energy, which is released as heat. The reaction is written as; C(graphite)(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + 393.5 Kj
ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS In an endothermic reaction, heat is absorbed. In this type of reaction equation, heat is noted on the reactants’ side (left). Decomposition of CaCO3 is a good example of an endothermic reaction, where its equation is expressed as follows:
CaCO3(s) + 169.5 kJ → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Indicate the following reactions as endothermic or exothermic reactions: a. 2Al(s) + Fe2O3(s) → 2Fe(s) + Al2O3(s) + 850 kJ b. H2(g) + I2(g) + 54 kJ → 2HI(g) c. CO(g) + 1/2O2(g) → CO2(g) + heat d. CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + heat → CH4(g) + 2O2(g) e. N2O(g) + H2(g) → N2(g) + H2O(l) + energy
|