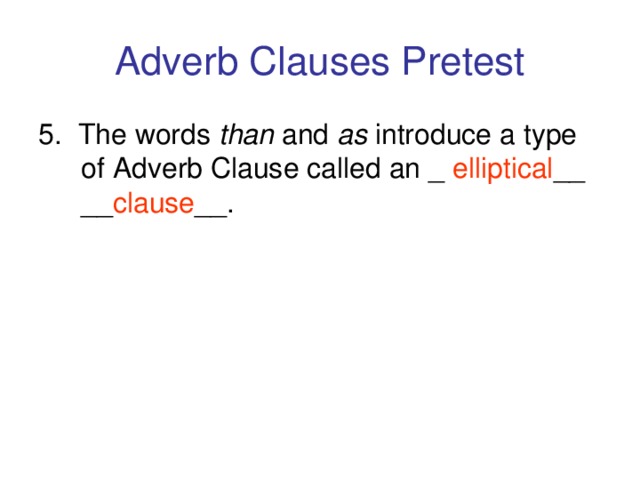
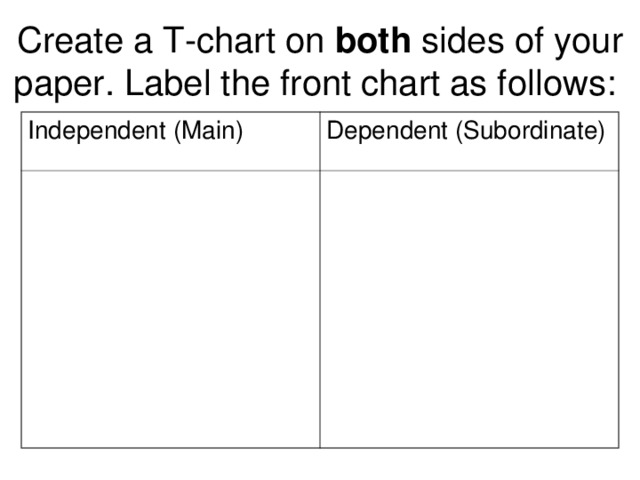
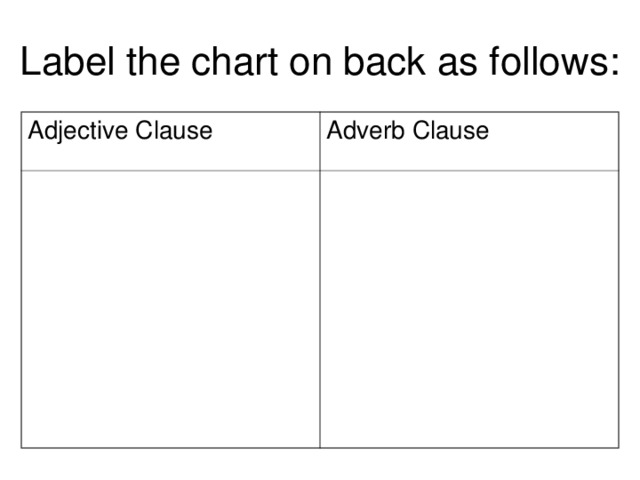
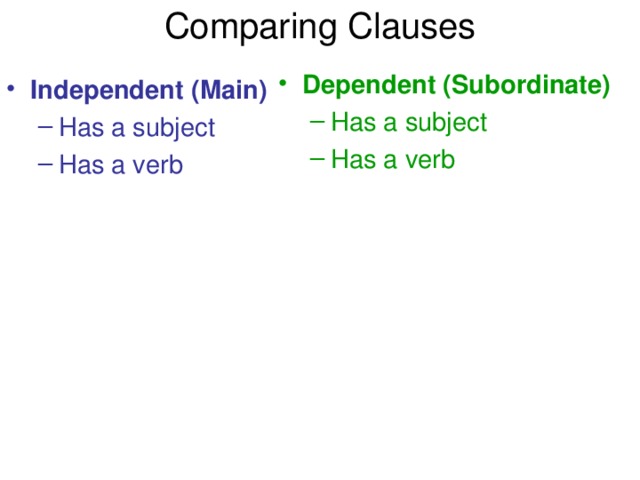
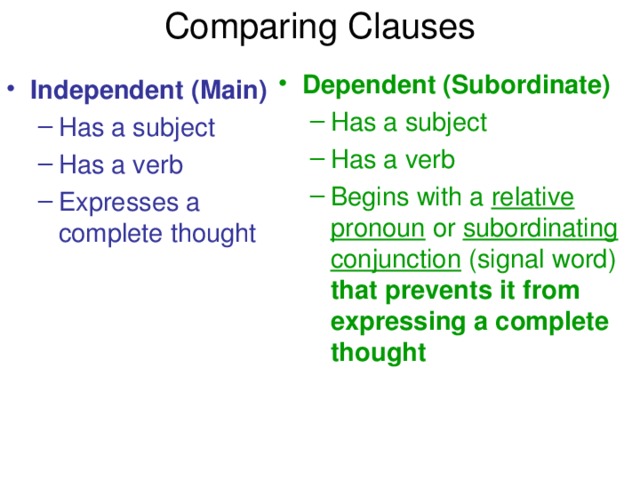
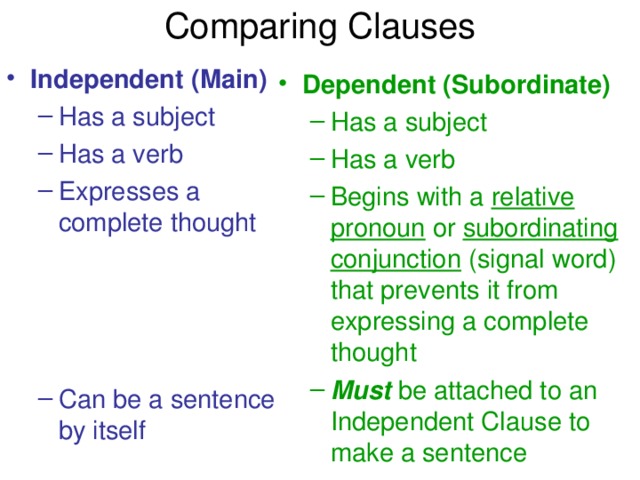
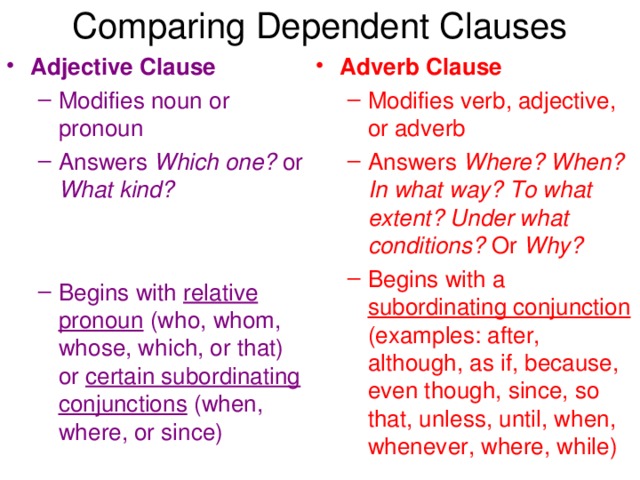
А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big
А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big
А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big
А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big
А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big
А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big
А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are bigА?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big А?ылшын тілінде зат есім екіге б?лінеді. Саналатын
ж?не саналмайтын зат есімдер.
Саналатын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келетін, жекелеп саналатын зат есім.
Мыс: a book, an apple
Саналмайтын зат есім дегеніміз - ?олмен ?стау?а
келмейтін, жекелеп саналмайтын с?йы? заттарды
атаймыз. Мыс : a water, a milk, a sugar
Саналатын зат есімдер жекеше ж?не к?пше т?рде ?олданылады. Those bags are big