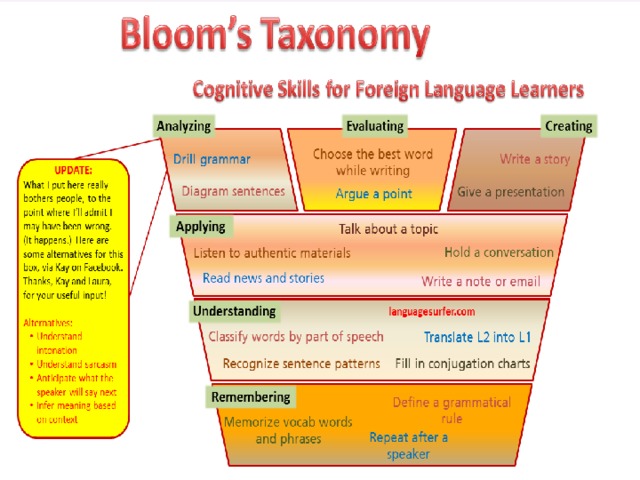
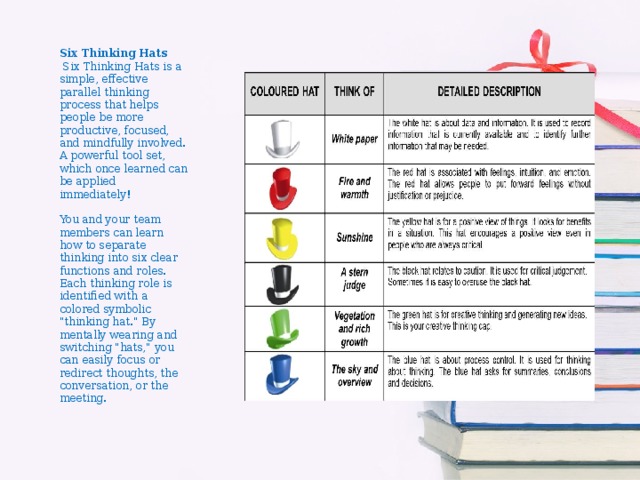
•Origins of the term The term ‘Critical Thinking’ first started emerging in academic circles and literature in the midtwentieth century. In 1941, the academic Edward M. Glaser stressed that critical thinking referred to the search for evidence to support (or discredit) a belief or argument. In 1956, a committee of educators chaired by the educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom worked towards developing a system of thinking that would go beyond traditional rote learning in education and encourage ‘higher-order’ thinking. Although the taxonomy they devised is named after Bloom, it is a concept that has been refined and adapted over the years. However, at the core of Bloom’s Taxonomy is a series of skills that teachers should develop in their learners in order to make their students learn more effectively
Создайте Ваш сайт учителя Видеоуроки Олимпиады Вебинары для учителей
Презентация на тему "Critical Thinking in Language Classrooms"
Вы уже знаете о суперспособностях современного учителя?
Тратить минимум сил на подготовку и проведение уроков.
Быстро и объективно проверять знания учащихся.
Сделать изучение нового материала максимально понятным.
Избавить себя от подбора заданий и их проверки после уроков.
Наладить дисциплину на своих уроках.
Получить возможность работать творчески.
Просмотр содержимого документа
«Презентация на тему "Critical Thinking in Language Classrooms"»
Полезное для учителя
Распродажа видеоуроков!
1940 руб.
2770 руб.
1860 руб.
2660 руб.
1880 руб.
2690 руб.
1880 руб.
2690 руб.
ПОЛУЧИТЕ СВИДЕТЕЛЬСТВО МГНОВЕННО
* Свидетельство о публикации выдается БЕСПЛАТНО, СРАЗУ же после добавления Вами Вашей работы на сайт
Удобный поиск материалов для учителей
Проверка свидетельства